1. What is the CSS visibility property?
The CSS
property specifies the visibility of an HTML element.
Some of the values of the CSS
are:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| visible | shows the element |
| hidden | hides the element but space will be allocated to the element in the HTML document |
Example:
2. What is CSS Positioning?
The CSS
property defines the position of an HTML element in an HTML document. There are five values the CSS
property can take. They are:
- static
- relative
- absolute
- fixed
- sticky
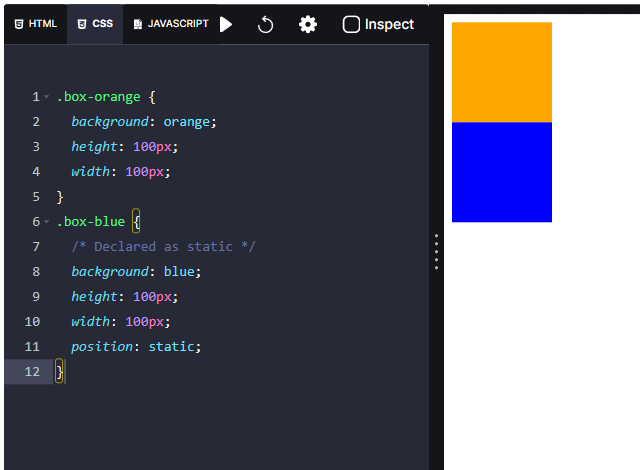
Static positioning
By default, HTML elements are positioned as static. This means that the HTML element is not affected by the
,
,
, and
CSS properties.
The
,
,
, and
properties are used with a position property to set the placement of an HTML element.
The element will generally move away from a given side when its value is positive and towards it when the value is negative.
As the HTML elements are positioned as
by default, the elements that we explicitly mention the
property value as
and doesn't mention the
property at all behave the same.
Relative positioning
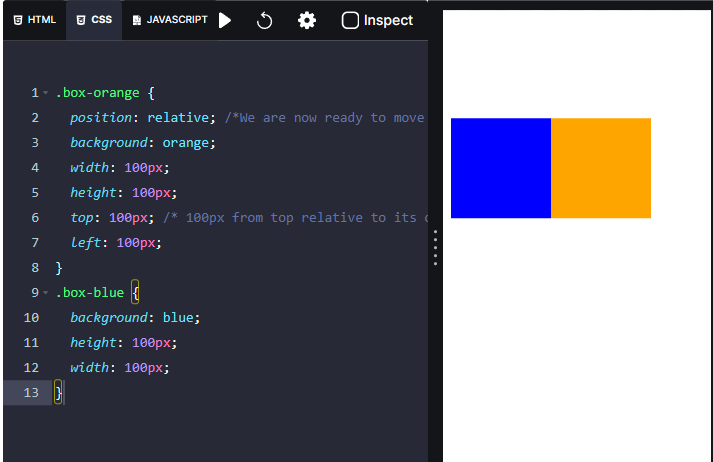
A relative positioned element is just like a static element but we can move it around from its default place.

If we notice the other content on the image, the element doesn't affect the document flow. That's why we say that this element is relative to itself.
Here the orange box will move away from the top
and left
from its default position. We can see that the orange box is beside the blue box in the preview.
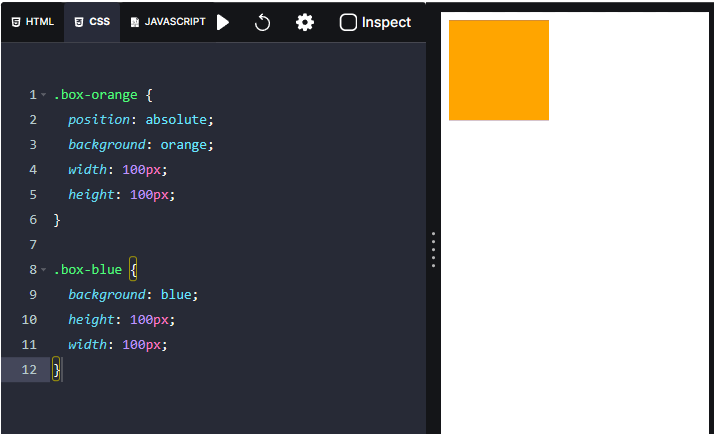
Absolute positioning
The absolute positioned elements are no longer part of the document flow. The other elements will ignore the absolute positioned element and re-flow accordingly.
They are positioned from their closest ancestor(closest parent) which has the
property value other than
. If no ancestor has a positioning, they are positioned from the viewport.

Now it looks like the blue box has disappeared, but it hasn’t. The blue box behaves like the orange box is removed, so it shifts up to the orange box’s place.
Fixed positioning

The fixed positioned elements are also no longer part of the document flow as absolute positioned elements. They are positioned relative to the screen’s viewport. The element does not move when the page is scrolled.
The position fixed will appear only if the page has scrolling.
Sticky Positioning

The sticky positioned elements will initially behave like
elements, but if we keep scrolling, they will get taken out of the normal flow and behave like
in their parent element.
This can be useful if we want to stick an element that's initially farther down the page to the top of the screen.
Here the top, bottom, left and right properties behave differently. When we set the top property(10px) to the position sticky element, the element will behave as relative until it reaches the 10px from the viewport and then it behaves as fixed in its parent container. Note Position Sticky is not supported in Internet Explorer and earlier versions of other browsers. 3. What is the default value of the CSS position property? The default value of the CSS position property is static. This means that the HTML element is not affected by the top, bottom, left, and right CSS properties.
CSS properties.
As the HTML elements are positioned as static by default, the elements that we explicitly mention the position static and doesn't mention the position property at all behave the same.
4. If an HTML container (div) element and an HTML paragraph element is given. How will you move HTML paragraph element to top left corner?
We can move the HTML paragraph element to top-left corner by applying,
CSS position property with value fixed or absolute to HTML paragraph element.
CSS top property and CSS left property with value 0 to HTML paragraph element.
5. What are the differences between relative positioning and absolute positioning?
| relative | absolute |
|---|---|
| HTML element is positioned from its default place | HTML element is positioned from the closest parent element which has position property other than static. If there is no positioned parent element, it is positioned from the viewport. |
| The default place of the HTML element remains in the flow of the document | The HTML element is removed from the flow of the document and other elements will behave as if it’s not present. |
6. What are the differences between fixed positioning and absolute positioning?
| fixed | absolute |
|---|---|
| HTML element is positioned from the viewport. | HTML element is positioned from the closest parent element which has position property value other than static. If there is no positioned parent element, it is positioned from the viewport. |
| The HTML element does not move when the page is scrolled. | The HTML element moves when the page is scrolled. |
| The HTML element is removed from the flow of the document and other elements will behave as if it’s not present. | The HTML element is removed from the flow of the document and other elements will behave as if it’s not present. |
7. What are the differences between fixed positioning and sticky positioning?
The sticky positioned elements will initially behave like
elements, but if you keep scrolling, they will get taken out of the normal flow and behave like
wherever you have positioned them in their parent element.
8. Explain the different types of CSS Selectors?
The different types of CSS Selectors are:
Simple Selectors
- Class Selector
- ID Selector
- Type (tag name) Selector
- Universal Selector
- Attribute Selector
- Pseudo-classes
- Pseudo-elements
- Combinators
Simple Selectors
| Selector | Description |
|---|---|
| Type(Tag name) | Selects all the elements of a given type(tag name) |
| Class | Selects all the elements of a given class name |
| ID | Selects all the elements of a given id |
| Universal | Selects all the elements in an HTML document |
Attribute Selector
The CSS Attribute Selector is used to select the HTML elements of a specified attribute or a specified attribute and value.
Examples:
- With Attribute name
- With both Attribute name and value
Pseudo-classes
A CSS pseudo-class specifies a special state of the selected elements. Some of the CSS Pseudo-classes are
,
,
, etc.
Example:
Pseudo-elements
A CSS Pseudo-element is used to style a specific part of the selected element. Some of the CSS Pseudo-elements are
,
,
, etc.
Example:
9. What are CSS Pseudo-classes?
A CSS pseudo-class specifies a special state of the selected elements.
A pseudo-class can't exist on its own. It must be attached to a CSS selector. The pseudo-class will only define a particular state of that selector.
Syntax:
Some of the common CSS Pseudo-classes are:
| Pseudo-class | Description |
|---|---|
| :hover | CSS properties will be applied if the selected element has hovered |
| :visited | CSS properties will be applied if the link is visited |
| :focus | CSS properties will be applied if the selected element is focused |
| :first-child | CSS properties will be applied if the selected element is first of its siblings |
| :last-child | CSS properties will be applied if the selected element is the last of its siblings |
10. What are CSS Pseudo-elements?
A CSS Pseudo-element is used to style a specific part of the selected element.
For example, it can be used to:
- Style the first letter or first line of an HTML element
- Insert content before or after the content of an HTML element
Syntax:
Some of the common CSS Pseudo-elements are:
| Pseudo-element | Description |
|---|---|
| ::first-line | CSS properties will be applied to the first line of the content in the selected element |
| ::first-letter | CSS properties will be applied to the first letter of the content in selected element |
| ::before | Content will be inserted before the content of a selected element |
| ::after | Content will be inserted after the content of a selected element |
11. How to apply CSS Properties by child number?
We can apply CSS properties by child number using the CSS
selector.
The CSS
pseudo-class selects the HTML elements based on the position among their siblings.
Example:
takes a single argument. It might be a number or keyword (even, odd) or formula (2n).
12. How to style the visited and unvisited links using CSS?
We can style the visited and unvisited links with the CSS pseudo-classes
and
.
Unvisited links: Using
or other selectors like tag, class name, etc.
Visited links: Using
All the visited links will be in green color whereas all unvisited links are in red color.
13. How to wrap a block of text around the HTML image element?
We can wrap a block of text around the HTML image element using the CSS
property.
Some of the values of the CSS
property are:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| none | (Default value) The element does not float (will be displayed just where it occurs in the text) |
| left | The element floats to the left of its container |
| right | The element floats to the right of its container |
Example:
14. Explain CSS Background Properties?
The CSS background properties let us control the size and properties of background images/colors.
Some of the CSS background properties are:
- background-image
- background-size
- background-repeat
- background-position
- background-origin
- background-clip
- background-attachment
- background-color
- background(Short hand)
Background Image
The CSS
property sets one or more background images on an HTML element.
Example:
Background Size
The CSS
property sets the size of the background image of an HTML element.
Some of the values of CSS
property are:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| cover | Scales the image to the smallest size while maintaining the same aspect ratio (width/height) and covers the entire width and height even if the image is cropped or stretched |
| contain | Scales the image to the largest size while maintaining the same aspect ratio (width/height) and shows the whole image, even if that leaves a little space to the sides or bottom |
| percentage | Sets the width and height of the background image with respect to the parent element. The first value sets the width, the second value sets the height. If only one value is given, the second is set to "auto". Example: "50% 50%" |
Example:
Background Repeat
The CSS
property sets how a background image is repeated.
Some of the values of CSS
property are:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| repeat | (Default value) The background image is repeated both vertically and horizontally. The last image will be clipped if it does not fit. |
| no-repeat | The background image is not repeated. The image will only be shown once. |
Example:
Background Position
The CSS
property sets the initial position for the background image.
Example:
Background Origin
The CSS
property specifies the origin of the background image/ what the CSS
property is relative to.
Some of the values of CSS
property are:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| padding-box | (Default value) The background position of the image is relative to the padding box |
| border-box | The background position of the image is relative to the border box |
| content-box | The background position of the image is relative to the content box |
Background Clip
The CSS
property specifies how far the background should extend within an HTML element.
Some of the values of the CSS
property are:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| border-box | (Default value) The background extends behind the border |
| padding-box | The background extends to the inside edge of the border |
| content-box | The background extends to the edge of the content box |
Background Attachment
The CSS
property specifies the behaviour of the background image when the page is scrolled.
Values of the CSS
property are:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| scroll | background image scrolls along with the HTML element. |
| fixed | background image doesn't scroll with the HTML element. It will be fixed with the viewport. |
Background Color
The CSS
property specifies the background color of an HTML element.
Background
The CSS
property sets all background style properties at once, such as color, image, origin and size, or repeat method.
It is a shorthand property for the below CSS properties:
- background-attachment
- background-clip
- background-color
- background-image
- background-origin
- background-position
- background-repeat
- background-size
15. What is the CSS direction property?
The CSS
property sets the direction of text, table columns, and horizontal overflow in an HTML block-level element.
Some of the values of CSS
property are:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| ltr | (Default value) Text and other elements go from left to right |
| rtl | Text and other elements go from right to left |
Example:
16. How to align the last line of a text?
The CSS
property specifies the horizontal alignment of the last line of a text in an HTML element.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| center | Aligns the last line of a text to the center |
| left | Aligns the last line of a text to the left |
| right | Aligns the last line of a text to the right |
Example:
17. How to add inner shadows to an HTML element?
The CSS
property adds shadow to an HTML element.
By default, the shadow is a drop shadow (shadow seems raised above the content).
To add an inner shadow, we need to specify the
keyword along with the other values like
,
, etc.
Example:
18. What are CSS custom properties?
A CSS custom property is most commonly thought of as a variable in CSS.
It is set using a custom property notation (e.g.
) and are accessed using the
function (e.g.
).
If the custom property has to be accessed through the entire HTML document, declare it inside the
19. What is the CSS display property with the value inline-flex?
It is similar to the CSS
property with the value
.
Both convert the HTML element to a flex container. But the value
also converts the element (flex container) to an inline element.
Example:
Here the flex container doesn't start on a new line and takes only the content width.