React JS is an open-source JavaScript library used to build user interfaces. It was developed by Facebook.
1.1 Why React JS?
- Performant websites
- Fewer lines of code
- Improves readability of code
- Less time consuming
- Open Source
- Reusable code
1.2 Advantages of React JS
- Easy to Learn
- Large Community
- Developer Toolset
2. Running JavaScript in HTML
We can run JavaScript in HTML using the HTML
Here the
To include an external JavaScript file, we can use the HTML
When the browser comes across a
So, we need to put a
If more than one
3. Creating Elements using React JS
3.1 React CDN
3.2 React.createElement()
The
Syntax:
type - Tag names like
Props are shorthand for properties. It is an optional argument.
3.3 ReactDOM.render()
The
Syntax:
reactElement - What to render container - Where to render
4. JSX
React JS introduced a new HTML like syntax named JSX to create elements.
The above JSX element compiles to,
4.1 Babel
JSX is not JavaScript. We have to convert it to JavaScript using a code compiler. Babel is one such tool.
It is a JavaScript compiler that translates JSX into regular JavaScript.
- For JSX, the typeattribute value of the HTMLscriptelement should betext/babel.
- For providing class names in JSX, the attribute name should be className.
Differences between HTML and JSX:
| HTML | JSX |
|---|---|
| class | className |
| for | htmlFor |
4.2 Embedding Variables and Expressions in JSX
We can embed the variables and expressions using the flower brackets
Embedding variables in JSX:
Embedding Expressions in JSX:
4.3 Nesting JSX elements
The
In this project, let's build a Super Over League by applying the concepts we have learned till now.
Refer to the image below:

Design Files
Click to view
Completion Instructions
Implementation Files
Use these files to complete the implementation:
- index.js
- index.css
Resources
Image URLs
Colors
Font-families
- Roboto
Things to Keep in Mind
- Do not remove the pre-filled code
- Want to quickly review some of the concepts you’ve been learning? Take a look at the Cheat Sheets.
In this project, let's build a Congrats Card by applying the concepts we have learned till now.
Refer to the image below:
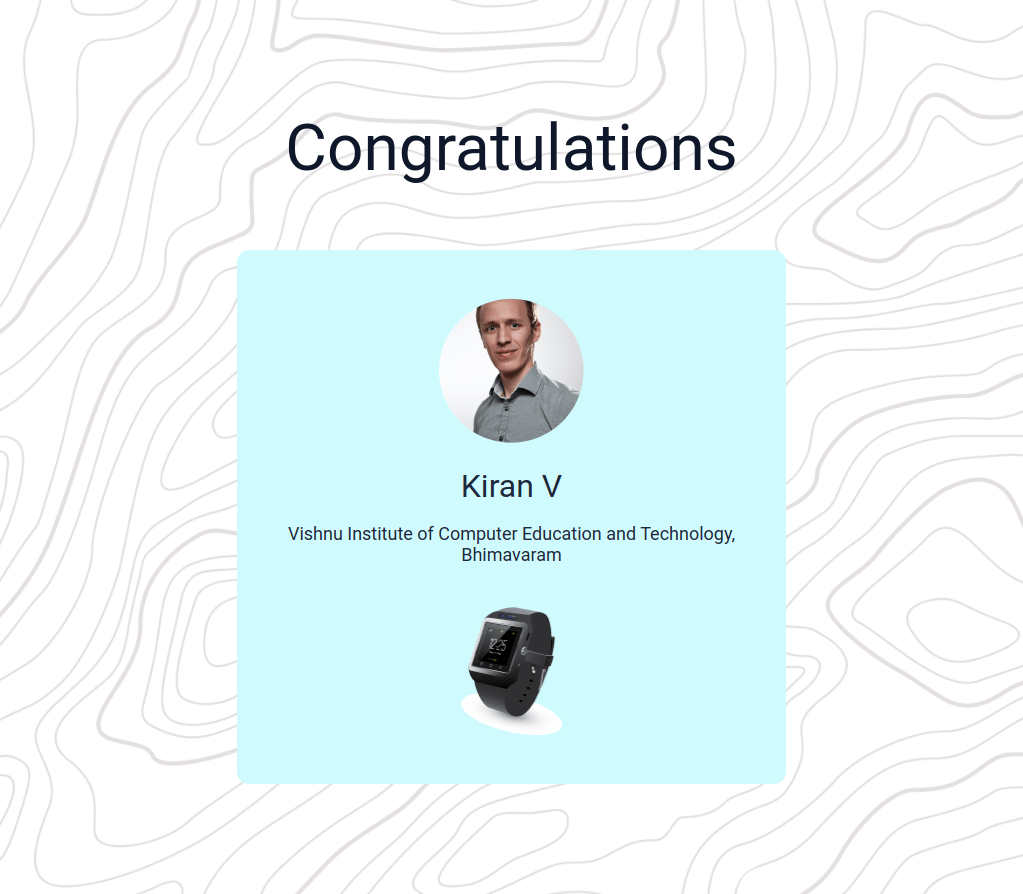
Design Files
Click to view
Completion Instructions
Implementation Files
Use these files to complete the implementation:
- index.js
- index.css
Resources
Image URLs
Colors
Font-families
- Roboto
Things to Keep in Mind
- Do not remove the pre-filled code
- Want to quickly review some of the concepts you’ve been learning? Take a look at the Cheat Sheets.
